CAPM Exam & PMP Exam Study Notes:
Project Resource Management
Written By: Alvin the PM | Last Updated: June 12, 2021
Topic: CAPM Exam & PMP Exam Certification Study Notes
Listed below are my CAPM Exam & PMP Exam Study Notes for Project Resource Management that I’ve used to pass my own CAPM Exam, and which I also intend to use for my 2021 PMP Exam Preparation.
If you find any of my website notes and Youtube Videos helpful to pass your CAPM Exam or PMP Exam, considering supporting me by buying me a cup of “virtual” coffee by clicking the below link.
❤️ SUPPORT Alvin the PM by buying me “virtual” coffee ❤️
Please Note: These notes are meant to be a supplementary aid, and not as your primary study material for your CAPM Exam and/or PMP Exam. This is meant to help clarify any confusing topics and explain the most challenging concepts which are difficult to understand & remember. Please reference your own Exam Prep Book or your PMBOK Guide for further detail.
I’ve listed the Knowledge Area below, with an explanation of the following:
1) Overview of each Process Group
2) Reference Section & Page in PMBOK 6th Edition
3) ITTO Summary & Analysis (Input, Tool, Technique, Output)
>> Any items marked with an * asterisk are the unique ones & critical topics to master
4) Key Concepts & Helpful Exam Prep Information
Overview of Resource Management
Resource Management is split up into the following six (6) Process Groups:
1) Plan Resource Management (PL)
2) Estimate Activity Resources (PL)
3) Acquire Resources (EX)
4) Develop Team (EX)
5) Manage Team (EX)
6) Control Resources (M&C)
Purpose: Understanding what resources are needed to successfully execute your project, and acquiring & managing these resources
>>Alvin’s Exam Tip:
Alvin the PM
This Knowledge Area can be confusing and really easy to mix up with Procurement Management and Stakeholder Management…
So, just think of Resource Management as: What resources do you need (physical or personnel) and how will you procure & manage them?
Remember… Resource Management is focused on BOTH the Team and Physical Resources.
Key Concepts:
1. What is the difference between Physical and Team Resources?
– Physical Resources = Supplies, Materials, tools, equipment, facilities, software, cloud/IT, databases
– Personnel/Team Resources= Human resources (e.g. Engineers, Supply Chain Buyers, Analysts, Manufacturing Specialists)
2. What are the factors which can influence the management & development of a team?
– Environment and locations of your Team members
– Organization’s change management, culture, and politics
– How stakeholders communicate with each other
Process #1: Plan Resource Management
1.1 Resource Management: Plan Resource Management (PL)
– Pg. 312, PMBOK 6th Edition
Purpose: Developing the Resource Management Plan for how to manage your resources. Think of this as the first step for Planning your Resources…
How will you make sure that you have enough resources to launch your project to 100% completion?
In other words, what process will you follow to estimate/determine the resources needed, and ultimately, to procure and manage these resources?
ITTO Analysis: Plan Resource Management
1) What do You Need? (Input)
– Project Charter, Project Management Plan, Project Documents, EEF/OPA
>> Project Management Plan: Quality Management Plan, Scope Baseline
>> Project Documents: Project Schedule, Requirements Documentation, Risk Register, Stakeholder Register
2) What is the Result? (Output)
– *Resource Management Plan, *Team Charter, Updates to Project Documents
3) How Do You Accomplish It? (Tool/Technique)
–*Organizational Theory; Expert Judgment; Meetings; Data Representation
>> Data Representation: *Responsibility Assignment Matrix, *Hierarchical Charts, and *Text-oriented Formats
Key Concepts:
Resources are limited, and oftentimes, may compete for priority.
This of course, impacts your project’s costs, schedule, and risks, and are all critical factors to consider when you’re planning your project.
As a Project Manager, it’s your responsibility to determine if you have enough resources to support your project’s work, and to plan accordingly for the availability and/or scarcity of these resources.
Key Terms to Remember:
1. Data Representation Techniques
Hierarchical Charts – This is a graphical, top-down graphic showing positions and responsibilities of each team member, or a hierarchical list of team & physical resources based upon category and resource type.
>>Example: Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), Organizational Breakdown Structure (OBS), and Resource Breakdown Structure
Text-oriented Formats – Outlined descriptions of the job positions and responsibilities of each team member
Responsibility Assignment Matrix, RAM – Shows the connection between Work Packages/ActivitIes and Team Members.
>> The most commonly used RAM is known as a RACI Chart
RACI Chart Example
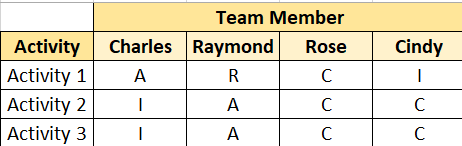
R = Responsible: Who is the one actually performing the work?
A = Accountable: Typically, only one person is held Accountable for the completion of an activity. For example, the Engineer’s Manager.
C = Consult: Who are Subject Matter Experts or other team members you can reach out to while working on the execution of this task?
I = Inform: Who do you notify that the work is being completed?
2. Organizational Theory – This explains how people and teams behave and interact with each other.
3. Resource Management Plan – This Plan contains information for how we will identify, procure and manage our resources.
What’s inside the Resource Management Plan?
Alvin the PM
1 – How resources will be determined and acquired
2 – Roles & Responsibilities
3 – Organization Charts
4 – Guidance for how resources will be managed and released from the project
5 – Development and training of the team
6 – Description of how team members will be rewarded and recognized for their efforts
7 – Controlling of Resources – How do we make sure that resources are available when needed?
4. Team Charter – This defines the expectations of what is accepted from each team member, and in so doing, helps increase the team’s cohesiveness and productivity
>> What are the team’s guidelines (communications & etiquette for holding meetings), values (code of conduct), principles, and processes to follow (making decisions, and resolving conflict)
Process #2: Estimate Activity Resources
1.2 Resource Management: Estimate Activity Resources (PL)
– Pg. 320, PMBOK 6th Edition
Purpose: Determining the resources you need (staff, material, supplies, equipment) to execute the project.
During this process, you’ll be creating a Resource Breakdown Structure outlining the resources (qty and type) you need to perform your project’s activities, as well as a list of your Resource Requirements and your Basis of Estimates.
ITTO Analysis: Estimate Activity Resources
1) What do You Need? (Input)
– Project Management Plan, Project Documents, OPA/EEF
>> Project Management Plan: Resource Management Plan, Scope Baseline
>> Project Documents: Activity Attributes & List, Logs (Assumption and Risk Register), Resource Calendars, Cost Estimates
2) What is the Result? (Output)
– *Resource Requirements, *Resource Breakdown Structure, *Basis of Estimates, Updates to Project Documents
3) How Do You Accomplish It? (Tool/Technique)
**Key Tools: Estimation Techniques (Bottom-up, Analogous, Parametric)
Other Tools: Expert Judgment, Data Analysis, PMIS, and Meetings
>> Data Analysis: Alternatives Analysis
Key Concepts:
This Process Group is performed simultaneously with Estimate Costs.
If for example, you need additional resources, you may want to hire a contractor to obtain the required technical knowledge, and you’ll also need to determine what those additional costs would be. Or, providing training to your Engineer so he/she can have the skillset needed to perform the more complex work.
(1) Estimation Techniques:
Bottom-up – Estimating resources at the activity level and then rolling this up to the Work Package Level)
Analogous – Leverage previous project’s for comparison
Parametric – Estimation technique that uses a statistical relationship between historical data. For example, it takes X # hours to complete work.
(2) Alternatives Analysis – Evaluate different options (e.g. make vs buy, using internal vs external resources, different equipment manufacturers, using different materials) and evaluating impact on project’s objectives (quality, cost, risk, and scope)
Key Terms to Remember:
1. Resource Requirements – What resources do you need to complete each activity? Qty & type?
2. Resource Breakdown Structure – Top-down graphical representation showing the resource categories needed to perform your project’s work, such as Labor, Material, Equipment, and Supplies
3. Resource Histogram – Compares the resources you need to their availability
Process #3: Acquire Resources
1.3 Resource Management: Acquire Resources (EX)
– Pg. 328, PMBOK 6th Edition
Purpose: This is the process for obtaining all the project’s required resources (personnel, equipment, material, supplies, tools). It’s during this process group that you’ll be assigning team members to their roles & responsibilities.
ITTO Analysis: Acquire Resources
1) What do You Need? (Input)
– Project Management Plan, Project Documents, OPA/EEF
>> Project Management Plan: Resource Management Plan, Procurement Management Plan, Cost Baseline
>> Project Documents: Project Schedule, Resource Calendars & Requirements, Stakeholder Register
2) What is the Result? (Output)
– *Physical Resource Assignments, *Team Assignments, *Resource Calendars, *Change Requests, Updates to Project Management Plan & Project Documents, Updates to OPA & EEF
3) How Do You Accomplish It? (Tool/Technique)
– *Virtual Teams, *Pre-assignment, Decision making, and Interpersonal & Team Skills
>> Decision Making; Multicriteria Decision Analysis
>> Interpersonal and Team Skills: Negotiation
Key Concepts:
1. Remember that resources you procure can be from either inside OR outside your company.
>> Internal Resources are obtained by Negotiating, using your Interpersonal and Team Skills, and working with the respective functional manager
>> External Resources are obtained through the procurement process.
Key Terms to Remember:
1. Pre-assignment – This is when you assign your stakeholders to your project IN ADVANCE
2. Virtual Teams – Team members who do NOT meet in-person and work remotely from each other.
3. Multicriteria Decision Analysis – This technique uses criteria to rate potential resources and which ones will be procured. Factors to consider include: Availability, cost, experience, location, skill level
4. Assignments: Team & Physical Resource Assignments
Physical Resource Assignments – This captures which physical resources will be used during the project: Equipment, materials, supplies
Project Team Assignments – Assigning the roles & responsibilities of your team members
5. Resource Calendars – What are the actual working business days that resources are available?
Process #4: Develop Team
1.4 Resource Management: Develop Team (EX)
– Pg. 336, PMBOK 6th Edition
Purpose: This is the process where you will improve your team dynamics, the team member’s competencies, and how they interact with each other.
What is the goal of Developing the Team? Promote teamwork, increase team morale and productivity, create an environment of team spirit
(1) Enhance the team’s technical knowledge (Helps drive project to successful completion)
(2) Create an environment of trust and openness (Less conflict and increased collaboration)
(3) Drive accountability and ownership from the team so they feel empowered to make decisions (Each person will want to do his/her best to contribute to the project’s success)
ITTO Analysis: Develop Team
1) What do You Need? (Input)
– Project Management Plan, Project Documents, OPA/EEF
>> Project Management Plan: Resource Management Plan
>> Project Documents: Project Schedule, Team Assignments, Resource Calendars, Lessons Learned, Team Charter
2) What is the Result? (Output)
*Team Performance Assessments, *Change Requests, Updates to Project Management Plan & Project Documents, Updates to OPA & EEF
3) How Do You Accomplish It? (Tool/Technique)
– *Colocation, *Communication Technology, *Individual & Team Assessments, *Recognition & Rewards, *Training, *Virtual Teams, Meetings, Interpersonal and Team Skills
>> Interpersonal and Team Skills: Conflict management, influencing, motivation, negotiation, team building
Key Concepts:
Tuckman Ladder – 5 Stages of Development
1) Forming – The ‘introduction’. Your Team Members meet each other and learn about the project and their assigned responsibilities & roles. Everyone is a little ‘shy’ in the beginning.
2) Storming – You are STARTING to work on the project now! Everyone starts looking into the work required for the project, and you begin taking technical decisions.
>> This is where the ‘storm’ hits, and people disagree, since the team members may not be collaborative or open to each other’s ideas. This makes the environment counterproductive.
3) Norming – This is the period where the team dynamics goes to ‘normal’ and everyone builds a normal relationship with each other.
>> Your Team now starts being collaborative and supporting & trusting each other. Your goal is to move from Storming to Norming as soon as possible, so that everyone trusts each other and works effectively.
4) Performing – This is when you have the DREAM TEAM and everyone is ‘performing’ at their best, like a well oiled machine! All issues are worked through independently. Think, Peak Performance!
5) Adjourning – Closing out the project and releasing the team members from the project.
Key Terms to Remember:
1. Team Charter – Outlines the guidelines for how the team will operate
2. Colocation: Place team members in the SAME location
3. Communication Technology – Shared portals, Audio/Video Tools, Email & Chat
4. Team Performance Assessments – These assessments are a way to evaluate your team’s performance – how well are we doing, collectively as a group? Note that this is the KEY output of the Develop Team process.
>> Use this evaluation to identify ways to improve your team’s behavior & performance. This could be coaching, training, and mentorship.
5. Individual and Team Assessments – These are tools to give you an idea of the strengths and weaknesses of your team members. Examples of assessments include: surveys, assessments, interviews, and ability tests.
6. Recognition and Rewards – Always consider cultural backgrounds when giving out rewards & recognition to your team members
Process #5: Manage Team
1.5 Resource Management: Manage Team (EX)
– Pg. 345, PMBOK 6th Edition
Purpose: Optimizing the the project’s performance by tracking each person’s performance, giving feedback, helping solve issues, and managing team changes.
In this process, you’re influencing the behavior of your Team through leadership, conflict management, and communication.
This focuses more on the HUMAN side of things.
ITTO Analysis: Manage Team
1) What do You Need? (Input)
– *Work Performance Reports, *Team Performance Assessments, Project Management Plan, Project Documents, OPA/EEF
>> Project Management Plan: Resource Management Plan
>> Project Documents: Logs (Issue Log, Lessons Learned), Team Assignments, Team Charter
2) What is the Result? (Output)
*Change Requests, Updates to Project Management Plan & Project Documents, Updates to EEF
3) How Do You Accomplish It? (Tool/Technique)
– *Interpersonal and Team Skills, PMIS
>> Interpersonal and Team Skills: Conflict management, influencing, leadership, emotional intelligence, decision making
Key Concepts:
Work Performance Reports
– These reports are the results/visual representation of the analyzed Work Performance Information
– Helps determine future resource requirements, recognition & rewards, and updates to resource management plan
Conflict Resolution Techniques – How do you resolve Conflict?
(1) Withdraw/Avoid – Avoiding and backing away from the situation. You’re retreating from a conflict, postponing the issue, and you’d like someone else to resolve the issue.
>> Example: Not responding to an email or phone call; Having another Manager help resolve conflict
(2) Smooth/Accommodate – Highlights the areas that everyone agrees upon and considers everyone’s viewpoint to maintain the relationship.
>> Goal is to maintain relationships within the team. More cooperative & less assertive.
>> Example: Repeating the areas that everyone agrees to
(3) Compromise/Reconcile – Keep everyone happy! This is a ‘middle-ground’ or neutral zone. Brings some satisfaction to everyone.
– Might temporarily solve the problem in the near-term, but could lead to problems in the future. Leads to ‘lose-lose’ outcome.
>> Example: Agree to one solution that was recommended by all teams.
(4) Force/Direct – Being an autocrat, where you force your view onto others.
– Leads to a win / lose situation. One person will feel like they lost.
>> Example: In a team discussion, deciding to follow the strategy from Management/HIPPO (i.e. the Highest Paid Person’s Opinion).
(5) Collaborate/Problem Solve – Best approach to solve conflicts. You need to have open dialogue in order to incorporate different viewpoints, and address everyone’s points. Leads to ‘win-‘win
>> Reaching a consensus
What are the sources of Conflict? 7 Sources of conflict in order from highest to lowest:
>>Schedule, Project priorities, Resources, Technical opinions, Administrative procedures, Cost, Personality
Key Terms to Remember:
1. Emotional Intelligence – Understanding your own emotions, as well as those around you on your team
2. Influencing – Project Managers have little to no authority over team members in a matrix-style organization; therefore, be persuasive, articulate your points, and build trust with your team
3. Leadership – Motivate your team for high performance
Process #6: Control Resources
1.6 Resource Management: Control Resources (M&C)
– Pg. 352, PMBOK 6th Edition
Purpose: Were the resources you planned actually available during the execution of the project? Do any corrective actions need to be implemented if there aren’t sufficient resources available? And, how does the actual usage of the resources compare to the planned resources? .
In contrast to Develop and Manage Team, which is focused on employee/staffing resources, Control Resources is focused on the availability of physical resources.
ITTO Analysis: Control Resources
1) What do You Need? (Input)
– Work Performance Data, Agreements, Project Management Plan, Project Documents, OPA
>> Project Management Plan: Resource Management Plan
>> Project Documents: Logs (Issue Log, Lessons Learned, Risk Register), Physical resource assignments, Project Schedule, and Resource Breakdown Structure & Requirements
2) What is the Result? (Output)
*Work Performance Information, Change Requests, Updates to Project Management Plan & Project Documents
3) How Do You Accomplish It? (Tool/Technique)
*Problem Solving, *Interpersonal and Team Skills, *PMIS, and Data Analysis
>> Data Analysis: Alternatives Analysis, Cost-benefit Analysis, Performance Reviews, Trend Analysis
>> Interpersonal and Team Skills: *Negotiation, *Influencing
Key Terms to Remember:
1. Resource Requirements – What are the physical resources which you need in your project?
2. Physical Resource Assignments – What is your planned usage for each physical resource?
3. Trend Analysis – How is our project performing with respect to time? Are we getting better or worse?
4. Work Performance Information
– By examining the resource requirements and how the resources were allocated for your project, how is the project going? Are all correct resources being used at the correct time for the correct tasks?
Conclusion
I hope you found the above information helpful with your Project Management Exam Prep Journey! If you found this useful, please feel free to SHARE and RECOMMEND this website with a friend. My goal is to help other Project Managers pass their own CAPM Exam and PMP Exam, and become Certified in Project Management.
Cheers, Alvin
